Introduction of TCP
There are
two transport layer protocols: TCP and UDP. TCP – Transmission control
Protocol and UDP – User Datagram Protocol. In this post, we will discuss
about TCP.
TCP
provides a connection-oriented. TCP provides process to process communication
through the port number. TCP provides reliable services; it means sender can
know that each packet reached at destination through the acknowledgement from
receiver. TCP provides flow control, error control and congestion control. TCP
does not support multicasting and broadcasting. It supports unicasting. The
unit of information passed by TCP to IP is called segment. TCP maintains a
checksum on its header and data. TCP must discard duplicate data. When TCP
transmits data between sender and receiver, it performs 3 phases. Which is as
follow.
Connection
Establishment – TCP uses 3-way handshaking technique to established a connection
between sender and receiver. This phase involves SYN, ACK and Window size.
Data
Transfer – In this phase, sender sends a data to destination.
Connection
Termination – When all the data transferred from sender to receiver, then sender
sends FIN packet to receiver to terminate the connection.
Requirement
of TCP:
TCP is
used when transfer small amount data in secure manner. TCP protocol assurances
the integrity of data sent across the network. High-level protocols that need
to transmit data all use TCP protocol.
TCP Header (TCP Segment Structure)
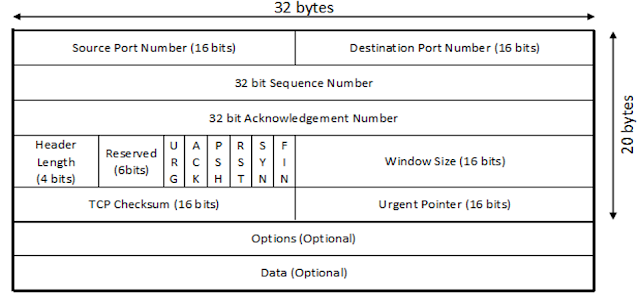 |
| Figure: TCP Header |
Above
figure shows the format of the TCP header. It’s also called TCP segment TCP
structure.
Source Port: It specifies the application sending the segment.
This is different from the IP address, which specifies an internet address.
Destination Port: It defines the receiving application port
numbers below 1023 called well-known ports are assigned to commonly used
application.
Sequence Number: Each byte in the stream that TCP sends is
numbered. It is used to arrange all the packets in a sequence at receiver side.
Acknowledgement Number: This field identifies the
sequence number of the next data by that the sender expects to receive if the
ACK bit is set.
Header Length: It specifies the length of the TCP header in
32-bit words.
Reserved: This field is reserved for future use and must be
set to 0.
There are 6 flags in TCP header: URG, ACK,
PSH, RST, SYN, FIN.
URG: The urgent pointer is valid if it set to 1.
ACK: ACK bit is set to 1 to indicate the
acknowledgement number valid.
PSH: The receiver should pass this data to the
application as soon as possible.
RST: This flag is used to reset the connection. It is
also used to reject an invalid segment.
SYN: Synchronization sequence number to initiate a
connection. The connection SYN = 1and ACK =0.
FIN: The FIN bit is used to release a connection. It
specifies that the sender is finished sending data.
Window Size: It specifies the number of bytes the receiver is
willing to accept. This field can be used to control the flow of data and
congestion.
Checksum: Used for transport layer error detection.
Urgent Pointer: If the URG flag bit is set, the segment
contains urgent data meaning the receiving TCP entity must deliver it to the
higher layers immediately.
Options: Size of this field is variable option field may be
used to provide other functions that are not covered by the header.
Data: Data field size is variable. It contains user
data.
Real time application of TCP
Chatting Application (Text Communication) – WhatsApp,
Instagram, Google hangouts, Telegram, iMessage, FB Messenger
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) – FileZilla,
Smart FTP, Core FTP, Fire FTP, Cyber duck and many more.
HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol) – HTTP uses TCP to access the webpages from internet. Ex., Website on internet. Facebook, Instagram etc…
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) – SMTP is an application layer protocol. It uses TCP protocol service to communicate with SMTP server. First of all, SMTP server accept connection request and then it allows the user to send mail. Ex., Yahoo mail, Gmail, Outlook, Rediff mail.
To learn more about TCP Header, Click here
Watch more videos click here.
No comments:
Post a Comment